As the popularity of erythritol as a sugar alternative continues to rise, many people are beginning to seek out new and innovative substitutes that can provide similar benefits without the drawbacks. In the quest for the perfect sweetener, understanding the different options available is crucial. Therefore, exploring alternative for erythritol not only caters to dietary preferences but also addresses various health considerations.
From natural plant-based sweeteners to other sugar alcohols, the landscape of sugar substitutes is evolving rapidly. Some of these alternatives boast minimal calories, low glycemic indexes, and unique flavor profiles that can enhance culinary creations. As consumers become more health-conscious and aware of the ingredients in their food, the search for viable replacements has become increasingly important.
In this article, we will delve into the best alternatives for erythritol that you need to try today. By examining their taste, health benefits, and how they can be incorporated into your daily diet, we aim to provide you with valuable insights. Embracing these alternatives not only opens a world of culinary possibilities but also supports a balanced and health-oriented lifestyle.

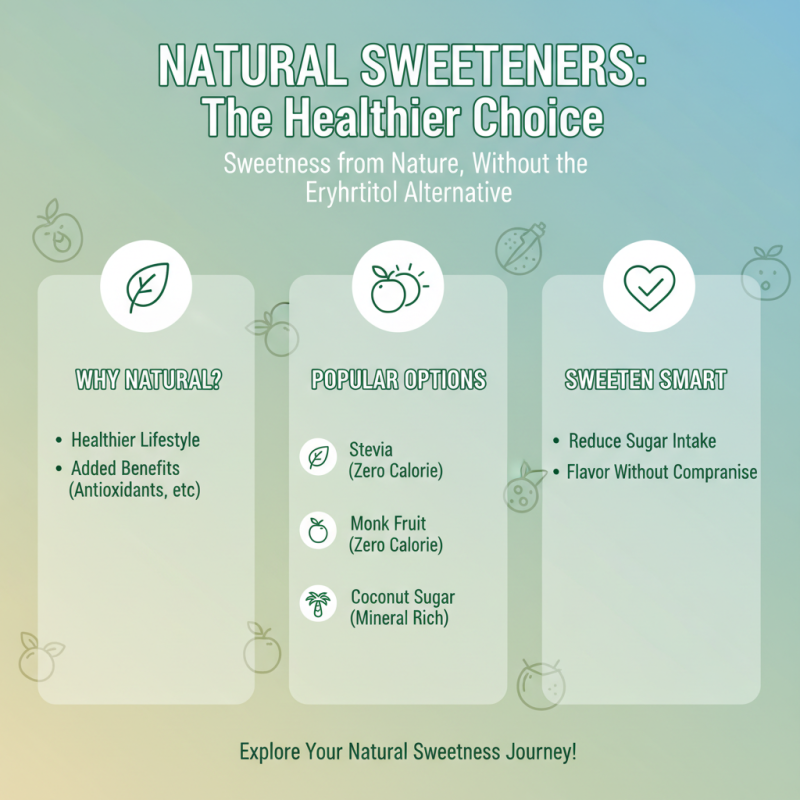
As people seek healthier lifestyles, the demand for natural sweeteners has surged, particularly as alternatives to erythritol. Natural sweeteners not only provide sweetness but often come with added health benefits, making them an appealing choice for those looking to reduce sugar intake without sacrificing flavor. Exploring options like stevia, monk fruit, and coconut sugar reveals a diverse array of choices for sweetening foods and beverages with a more natural touch.
Stevia, derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, is a popular choice due to its zero-calorie count and sweetness that can be up to 300 times that of traditional sugar. This makes it an excellent option for those managing their weight or blood sugar levels. Another excellent alternative is monk fruit, a sweetener made from the monk fruit extract that contains compounds called mogrosides, which offer sweetness without the calories and potential digestive issues associated with erythritol. Additionally, coconut sugar, made from the sap of coconut palm trees, provides a caramel-like flavor and retains some nutrients and trace minerals, making it a more wholesome choice for sweetening.
Whether used in baking, cooking, or as a sweetener in beverages, these natural alternatives can satisfy your sweet tooth while supporting a healthier lifestyle. By diversifying the sweeteners in your diet, you can enjoy the flavors you love without compromising on health.
The rising popularity of sugar alcohol substitutes has transformed the discussion around sweeteners, particularly as more consumers seek healthier alternatives to traditional sugar. Among various options, erythritol has gained attention due to its low-calorie content and minimal glycemic impact, but as we look towards 2025, several alternatives are emerging that can provide similar benefits. Recent industry reports indicate that the global market for sugar substitutes is projected to reach approximately $100 billion by 2025, reflecting an increasing awareness of health-conscious dietary choices.
One of the most notable health benefits of sugar alcohols is their ability to reduce caloric intake without sacrificing sweetness. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that erythritol, for instance, contains about 0.24 calories per gram, compared to sugar's 4 calories per gram. This significant reduction makes it an attractive option for individuals striving for weight management. Furthermore, research indicates that sugar alcohols like xylitol and maltitol can contribute to dental health, as they do not ferment in the mouth the same way sugar does, thus helping to prevent tooth decay.
Additionally, these sugar substitutes are often well-tolerated in terms of gastrointestinal effects, particularly when consumed in moderation. Data suggests that most individuals can safely consume moderate amounts without experiencing significant adverse reactions. As the demand for healthier sweetening options continues to surge, understanding the health benefits of these sugar alcohol substitutes will be crucial for consumers looking to make informed dietary choices.
This chart illustrates the top sugar alcohol substitutes and their average health benefits, showcasing their impact on blood sugar levels and calorie content. The data can help consumers make informed choices regarding these alternatives.
As more people seek healthier alternatives to sugar, plant-based sweeteners are gaining popularity for their natural origins and potential health benefits. One of the standout options in 2025 is monk fruit sweetener, derived from the monk fruit. This sweetener is not only zero-calorie but also has antioxidant properties, making it an appealing choice for those looking to reduce sugar intake without sacrificing sweetness.
Another noteworthy option is agave nectar, which is extracted from the agave plant. Its lower glycemic index compared to traditional sugar makes it suitable for individuals monitoring their blood sugar levels. Additionally, agave nectar has a unique flavor that can enhance various recipes, from baked goods to beverages, offering both versatility and a touch of natural sweetness.
Lastly, coconut sugar has emerged as a favorite among health-conscious consumers. Made from the sap of coconut palms, it retains some nutrients and has a lower glycemic index than regular sugar. Its rich caramel flavor can provide an exciting twist to many dishes, making it an excellent addition to a balanced diet while catering to those seeking plant-based options.
| Sweetener | Glycemic Index | Caloric Value (per 1 tsp) | Taste Profile | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stevia | 0 | 0 | Sweet, slightly bitter aftertaste | Beverages, desserts, baking |
| Monk Fruit | 0 | 0 | Sweet, mild flavor | Baking, beverages, sauces |
| Allulose | 0 | 0.4 | Similar to sugar | Baking, coffee, ice cream |
| Agave Nectar | 15 | 21 | Sweet, mild flavor | Dressings, beverages, baking |
| Coconut Sugar | 35 | 15 | Caramel-like flavor | Baking, sauces, toppings |
When considering sugar alternatives, especially in the context of
erythritol, it's crucial to analyze the caloric content of various options available today.
Erythritol itself is a low-calorie sugar alcohol, containing about 0.24 calories per gram, which is significantly lower than traditional sugar at 4 calories per gram. This characteristic has contributed to its popularity among those looking to reduce calorie intake without sacrificing sweetness.
In a broader context, other alternatives exhibit varying caloric profiles. For example, stevia, a plant-derived sweetener, contains zero calories, making it an attractive option for those aiming for a calorie-free sweetening choice.
A comparative report by the Food Ingredient Center shows that monk fruit extract also offers zero calories while providing a sweetness level up to 200 times that of regular sugar. However, it's essential to note that while these alternatives may have lower calories, their levels of sweetness can vary significantly, necessitating adjustments in recipes and usage.
The move towards these alternatives is part of a growing trend, as consumers increasingly seek healthier options. According to a recent market analysis, the low-calorie sweetener market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.3% over the next few years, driven by rising health concerns related to excessive sugar consumption. This trend emphasizes the importance of understanding the caloric content of various sweeteners for informed decision-making in dietary choices.
As more people look for healthier alternatives to sugar, the rise of various sweeteners has led to a wide selection of options. Incorporating new sweeteners into your diet can be a simple and effective way to reduce calorie intake without sacrificing flavor. However, knowing how to make these changes gradually can help ease your transition and enhance your overall experience.
One tip to incorporate new sweeteners is to start small. Instead of replacing all sugar in your recipes at once, try substituting a part of it with an alternative. This gradual approach allows your palate to adjust and ensures that you still enjoy your meals. For example, if you're baking, you might use half the usual sugar amount and replace it with a new sweetener to find a balance that suits your taste.
Another helpful strategy is to experiment with different sweeteners in various dishes. Some sweeteners work better in baked goods, while others shine in beverages or toppings. Don’t hesitate to explore and discover which ones you prefer in different contexts. By keeping an open mind and being willing to test out new combinations, you can find the perfect blend that satisfies your sweetness cravings while maintaining a healthier diet.